Infrared (IR) viewers
Main features
Application examples
- Description
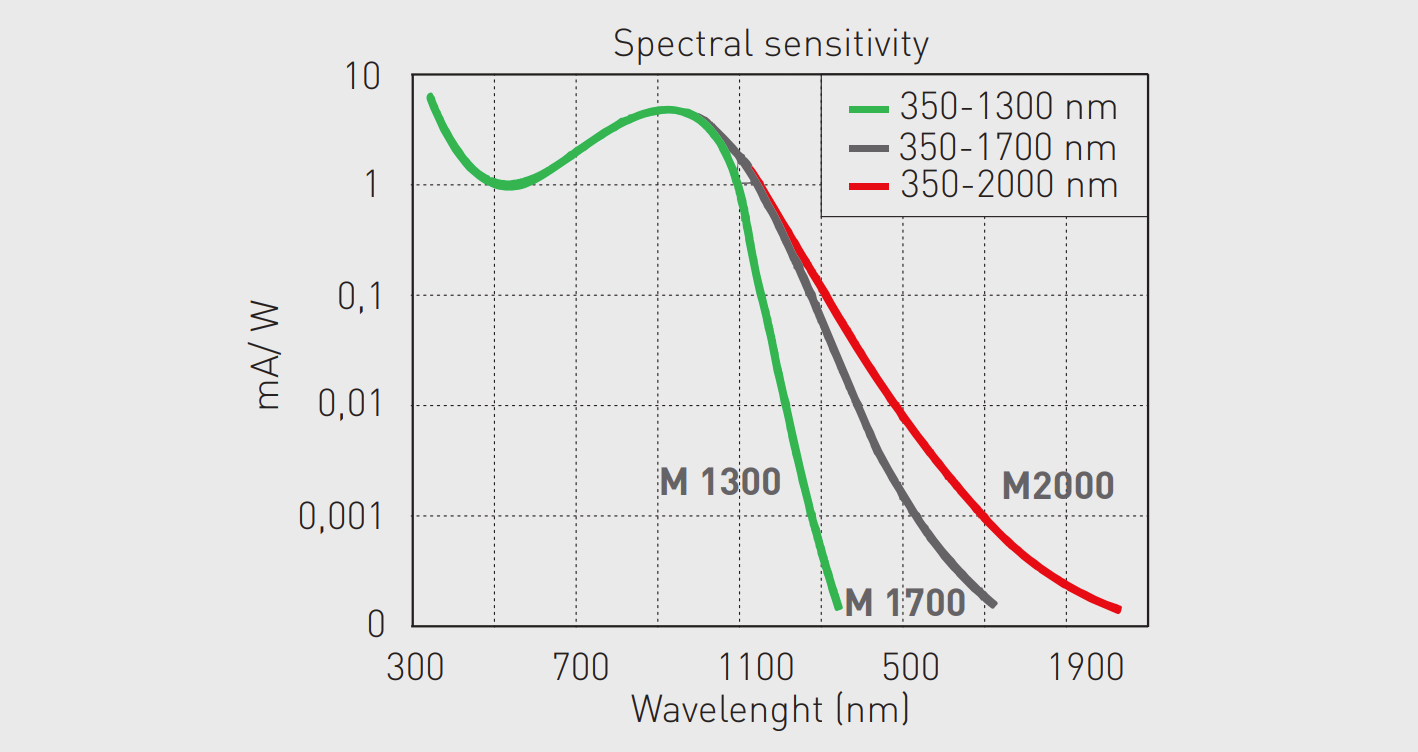
- Curves
- Standard specifications
- Additional accessories
- Downloads
Infrared (IR) viewers are used to observe, register, and record both indirect and direct radiation of IR lasers, light-emitting diodes (LED’s), dye, and other IR-sources. It is ideal for IR-laser beam alignment and inspection, optical fiber alignment, telecommunications, solar panel inspection, photo processing, surveillance and investigation in botany, biophysics, medicine, forensics and art restoration, infrared microscopy, fluorescence, etc. Digital version of IR viewer is based on multiphoton absorption (MPA) phenomenon when the wavelength of the laser exceeds the linear spectral detection range of the silicon material. In addition, the process of photoelectrons requires spatial and temporal filtering from noise to enhance the visualization of IR photons beyond the 1,1µm spectrum. By adjusting the gain on a pixel-by-pixel basis, it is possible to achieve imaging up to 1,7µm.
What’s in the box?
| IR-viewer specifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Model 1X | Model 2X | |
| Spectral range | 400-1700 nm | |
| Field of view | 38 deg | 19 deg |
| Magnification | 1X | 2X |
| Focus | 0,1 m to ∞ | 0,5 m (0,15m)* to ∞ |
| Objective lens | F1.3/8 mm | F1.4/16 mm |
| Adjustable iris | Included | |
| Resolution (center) | 60 Lp/mm | |
| Distortion of image | <1% | |
| Battery life fully charged | 10h, continuous | |
| Dimensions | 153 x 175 x 51 mm | |
| Tripod or handle | R1/4” | |
| IR-viewer accessories | |
|---|---|
| Neutral density filter to lens (3-5%@1064nm) | 99 eur |
| Facemask for hands free operation of IR Handheld viewer | 349 eur |
| C-mount camera adapter to IR Handheld viewer | 299 eur |
| Video adapter VA-1 adapter to IR Handheld viewer | 549 eur |
| Lens 2X (F1.8/50mm) | 299 eur |
| Lens 1X (F1.4/25mm) | 245 eur |
| Macro/distance ring | 49 eur |
| C-mount ring for any CCD lenses | 49 eur |
2D drawings:
